Compact Water Treatment Systems
The Filter Project compact water treatment plants are composed of a multi-step filtration process. To see more information regarding the water treatment process overview, hover over the number on the image below. You can read about some of the aspects of the process by clicking the number that represents the task in the image.
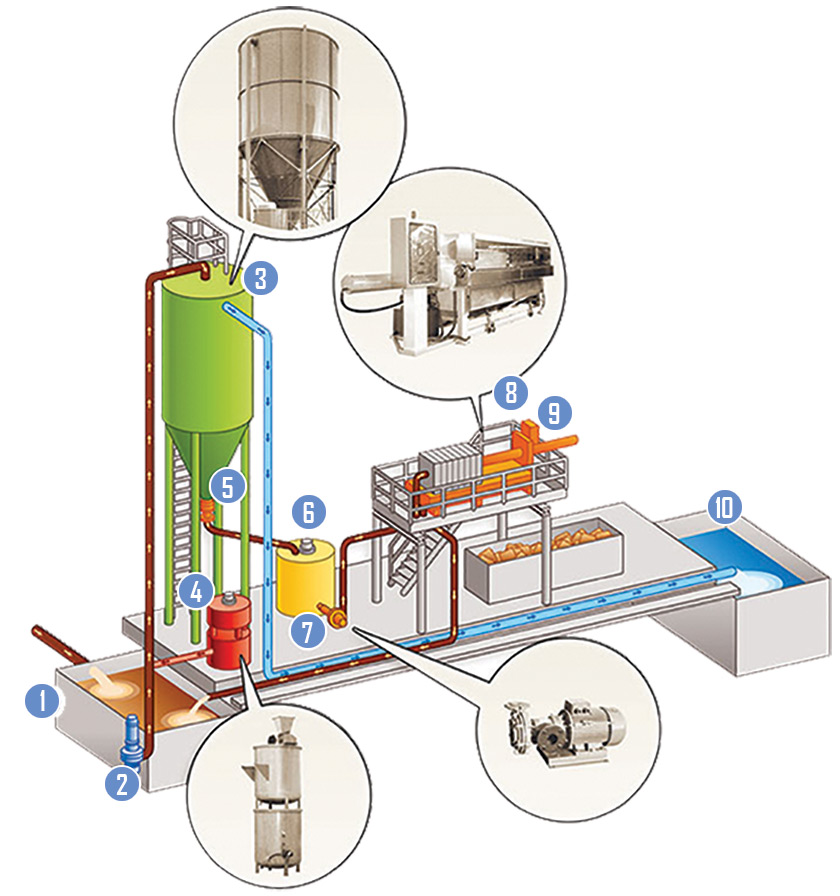
This part of the water treatment process consists of the waste water being introduced to the water treatment system. The water coming from the fabrication area are dispensed into the collection tank to be circulated through the treatment process.
The waste water is not left in the collection tank perpetually. After being collected, it is then moved from the collection tank to the clarifier by means of the submersible pump labeled here.
The clarifier is designed to remove solids by means of sedimentation. The prepared waste water (carrying polyelectrolytes from the dosing units) comes into the clarifier and separates by means of sedimentation. The clarified water is dispensed from the top, while the mud settles to the bottom.
The purpose of the part of the process labeled 4 is to assist the clarifier. This preparation and dosing station produces the polyelectrolyte that is sent into the waste water lifting pipe as it sends the water up.
The pneumatic valve here discharges the mud (solid substances) that have settled to the cone section of the clarifier. This valve discharges the mud into the mud collecting tank.
The mud collecting tank is the first stop for the “mud” after it is discharged from the clarifier. This tank is used as a resevoir for the “sludgey” substances so they can be sent to the filter press.
Moving the sludge from the mud storage tank to the filter press is done by means of the pump located here.
The filter press plays a key role in the water treatment process. This step is where the solid stone particles get extracted from the sludge that was produced by the clarifier; further separating the particles from the water.
This is the control panel that automatically controls the whole system which is managed by a self-diagnostic PLC.
This is were the clarified water is stored when it comes out of the clarifier in position 3. This water is recycled by sending it back into the fabrication shop for reuse.
